Page 4 - Delicado_Machordom_2015
P. 4
Evolutionary patterns of Pseudamnicola D. Delicado et al.
A
B
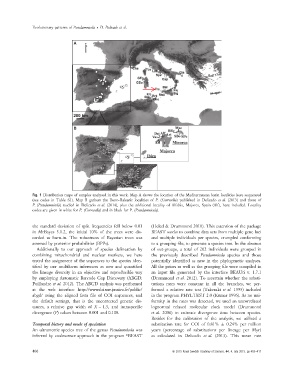
Fig. 1 Distribution maps of samples analysed in this work. Map A shows the location of the Mediterranean basin localities here sequenced
(see codes in Table S1). Map B gathers the Ibero-Balearic localities of P. (Corrosella) published in Delicado et al. (2013) and those of
P. (Pseudamnicola) studied in Delicado et al. (2014), plus the additional locality of Alfabia, Majorca, Spain (Alf), here included. Locality
codes are given in white for P. (Corrosella) and in black for P. (Pseudamnicola).
the standard deviation of split frequencies fell below 0.01 (Heled & Drummond 2010). This extension of the package
in MrBayes 3.1.2, the initial 10% of the trees were dis- BEAST works to combine data sets from multiple gene loci
carded as burn-in. The robustness of Bayesian trees was and multiple individuals per species, crumpled conforming
assessed by posterior probabilities (BPPs). to a grouping file, to generate a species tree. In the absence
Additionally to our approach of species delineation by of out-groups, a total of 202 individuals were grouped in
combining mitochondrial and nuclear markers, we here the previously described Pseudamnicola species and those
tested the assignment of the sequences to the species iden- potentially identified as new in the phylogenetic analyses.
tified by our multilocus inferences as new and quantified All the priors as well as the grouping file were compiled in
the lineage diversity in an objective and reproducible way an input file generated by the interface BEAUti v. 1.7.1
by employing Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery (ABGD: (Drummond et al. 2012). To ascertain whether the substi-
Puillandre et al. 2012). The ABGD analysis was performed tutions rates were constant in all the branches, we per-
at the web interface http://wwwabi.snv.jussieu.fr/public/ formed a relative rate test (Takezaki et al. 1995) included
abgd/ using the aligned fasta file of COI sequences, and in the program PHYLTEST 2.0 (Kumar 1996). As no uni-
the default settings, that is the uncorrected genetic dis- formity in the rates was detected, we used an uncorrelated
tances, a relative gap width of X = 1.5, and intraspecific lognormal relaxed molecular clock model (Drummond
divergence (P) values between 0.001 and 0.100. et al. 2006) to estimate divergence time between species.
Besides for the calibration of the analysis, we utilized a
Temporal history and mode of speciation substitution rate for COI of 0.81% 0.24% per million
An ultrametric species tree of the genus Pseudamnicola was years (percentage of substitutions per lineage per Myr)
inferred by coalescence approach in the program *BEAST as calculated in Delicado et al. (2013). This mean rate
406 ª 2015 Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, 44, 4, July 2015, pp 403–417