Page 4 - Dolphin_Tuna_Shark_1996
P. 4
22 K. Kannan et al.
MBT
Blubber
Bottlenose dolphin
Liver
Muscle
Bluefin tuna
" Liver
Fat
Blue shark
Liver
Kidney
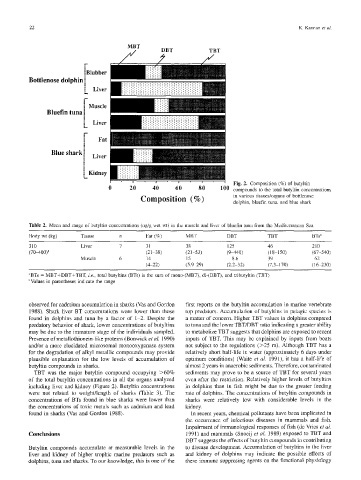
' Fig. 2. Composition (%) of butyltin
0 20 40 60 80 100 compounds to the total butyltin concentrations
• --
-,C'om"os:*:on (%) in various tissues/organs of bottlenose
v
dolphin, bluefin tuna, and blue shark
Table 2. Mean and range of butyltin concentrations (ng/g wet wt) in the muscle and liver of bluefin tuna from the Mediterranean Sea
Body wt (kg) Tissue n Fat (%) MBT DBT TBT BTs"
310 Liver 7 31 38 125 46 210
(70-400) b (21-38) (21-53) (9-440) (18-150) (67-540)
Muscle 6 14 15 8.6 39 62
(4-22) (5.9-29) (2.2-32) (7.3-I 70) (16-230)
"BTs = MBT+DBT+TBT, i.e., total butyltins (BTs) is the sum of mono-(MBT), di-(DBT), and tributyltin (TBT)
b Values in parentheses indicate the range
observed for cadmium accumulation in sharks (Vas and Gordon first reports on the butyltin accumulation in marine vertebrate
1988). Shark liver BT concentrations were lower than those top predators. Accumulation of butyltins in pelagic species is
found in dolphins and tuna by a factor of 1-2. Despite the a matter of concern. Higher TBT values in dolphins compared
predatory behavior of shark, lower concentrations of butyltins to tuna and the lower TBT/DBT ratio indicating a greater ability
to metabolize TBT suggests that dolphins are exposed to recent
may be due to the immature stage of the individuals sampled.
Presence of metallothionein-like proteins (Bonwick etaL 1990) inputs of TBT. This may be explained by inputs from boats
not subject to the regulations (>25 m). Although TBT has a
and/or a more elucidated microsomal monooxygenase system
for the degradation of alkyl metallic compounds may provide relatively short half-life in water (approximately 6 days under
plausible explanation for the low levels of accumulation of optimum conditions) (Waite et aI. 1991), it has a half-life of
butyltin compounds in sharks. almost 2 years in anaerobic sediments. Therefore, contaminated
TBT was the major butyltin compound occupying >60% sediments may prove to be a source of TBT for several years
even after the restriction. Relatively higher levels of butyltins
of the total butyltin concentrations in all the organs analyzed
including liver and kidney (Figure 2). Butyltin concentrations in dolphins than in fish might be due to the greater feeding
were not related to weight/length of sharks (Table 3). The rate of dolphins. The concentrations of butyltin compounds in
concentrations of BTs found in blue sharks were lower than sharks were relatively low with considerable levels in the
the concentrations of toxic metals such as cadmium and lead kidney.
found in sharks (Vas and Gordon 1988). In recent years, chemical pollutants have been implicated in
the occurrence of infectious diseases in mammals and fish.
Impairment of immunological responses of fish (de Vries et al.
1991) and mammals (Snoeij et al. 1989) exposed to TBT and
Conclusions
DBT suggests the effects of butyltin compounds in contributing
to disease development. Accumulation of butyltins in the liver
Butyltin compounds accumulate at measurable levels in the
and kidney of dolphins may indicate the possible effects of
liver and kidney of higher trophic marine predators such as
these immune suppresing agents on the functional physiology
dolphins, tuna and sharks. To our knowledge, this is one of the