Page 105 - Invasive_Species_2013
P. 105
Mediterranean invasive species factsheet
Similar species Having achieved such a widespread range over such
The body shape and filamentous middle rays a short period of time, F. commersonii is the fastest
distinguish this species from all other Mediterranean and farthest Lessepsian fish migrant ever recorded.
fishes. Young specimens (less than 20–30 cm long)
can be confused underwater with members of the Ecological impacts
The bluespotted cornetfish is an extremely voracious
Belonidae family; however, they can be
predator and is aggressive when in schools. It is one
distinguished from them by the long whip-like tail
of the top predators in the seas it has invaded,
filament. In addition, Belonidae species are more
feeding on fish fry and benthic fishes (adults of small
frequently observed in open water just below the sea
fish species or juveniles), including commercially
surface, while the bluespotted cornetfish is always
important Centracanthidae, Sparidae and Mullidae
closer to the bottom.
species, and a large number of gobiids. The spread
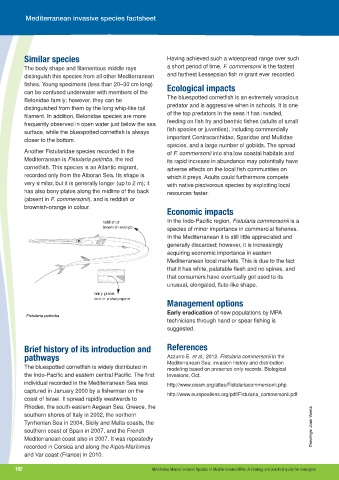
Another Fistularidae species recorded in the of F. commersonii into shallow coastal habitats and
Mediterranean is Fistularia petimba, the red its rapid increase in abundance may potentially have
cornetfish. This species is an Atlantic migrant, adverse effects on the local fish communities on
recorded only from the Alboran Sea. Its shape is which it preys. Adults could furthermore compete
very similar, but it is generally longer (up to 2 m); it with native piscivorous species by exploiting local
has also bony plates along the midline of the back resources faster.
(absent in F. commersonii), and is reddish or
brownish-orange in colour.
Economic impacts
reddish or In the Indo-Pacific region, Fistularia commersonii is a
brownish-orange species of minor importance in commercial fisheries.
In the Mediterranean it is still little appreciated and
generally discarded; however, it is increasingly
acquiring economic importance in eastern
Mediterranean local markets. This is due to the fact
that it has white, palatable flesh and no spines, and
that consumers have eventually got used to its
unusual, elongated, flute-like shape.
bony plates
end in a sharp spine
Management options
Early eradication of new populations by MPA
Fistularia petimba
technicians through hand or spear fishing is
suggested.
Brief history of its introduction and References
pathways Azzurro E. et al., 2012. Fistularia commersonii in the
Mediterranean Sea: invasion history and distribution
The bluespotted cornetfish is widely distributed in modeling based on presence-only records. Biological
the Indo-Pacific and eastern central Pacific. The first Invasions, Oct.
individual recorded in the Mediterranean Sea was http://www.ciesm.org/atlas/Fistulariacommersonii.php
captured in January 2000 by a fisherman on the
http://www.europealiens.org/pdf/Fistularia_commersonii.pdf
coast of Israel. It spread rapidly westwards to
Rhodes, the south-eastern Aegean Sea, Greece, the
southern shores of Italy in 2002, the northern
Tyrrhenian Sea in 2004, Sicily and Malta coasts, the
southern coast of Spain in 2007, and the French Drawings: Juan Varela
Mediterranean coast also in 2007. It was repeatedly
recorded in Corsica and along the Alpes-Maritimes
and Var coast (France) in 2010.
102 Monitoring Marine Invasive Species in Mediterranean MPAs: A strategy and practical guide for managers