Page 20 - Invasive_Species_2013
P. 20
Climate change and invasive
species interactions
Climate change will have significant impacts on coastal introduction of more Red Sea species into the south-eastern
zones, as it will drive the predicted rise in sea levels and sea Mediterranean and their rapid spread northwards and
and air temperatures and will also change other hydrological westwards. Similarly, it will also assist the spread of species
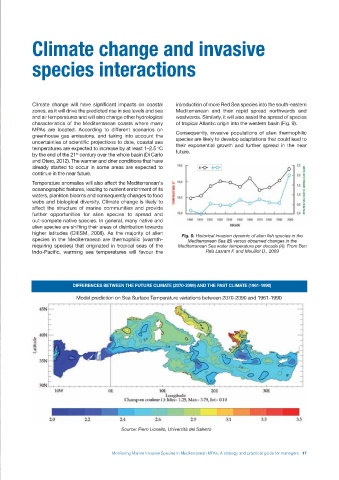
characteristics of the Mediterranean coasts where many of tropical Atlantic origin into the western basin (Fig. 9).
MPAs are located. According to different scenarios on
Consequently, invasive populations of alien thermophilic
greenhouse gas emissions, and taking into account the
species are likely to develop adaptations that could lead to
uncertainties of scientific projections to date, coastal sea
their exponential growth and further spread in the near
temperatures are expected to increase by at least 1–2.5 C
o
future.
by the end of the 21 century over the whole basin (Di Carlo
st
and Otero, 2012). The warmer and drier conditions that have
already started to occur in some areas are expected to
continue in the near future.
Temperature anomalies will also affect the Mediterranean’s
oceanographic features, leading to nutrient enrichment of its NEW RED SEA EXOTIC ARRIVALS/DECADE
waters, plankton blooms and consequently changes to food
webs and biological diversity. Climate change is likely to
affect the structure of marine communities and provide
further opportunities for alien species to spread and
out-compete native species. In general, many native and
alien species are shifting their areas of distribution towards
higher latitudes (CIESM, 2008). As the majority of alien
Fig. 9. Historical invasion dynamic of alien fish species in the
species in the Mediterranean are thermophilic (warmth- Mediterranean Sea (B) versus observed changes in the
requiring species) that originated in tropical seas of the Mediterranean Sea water temperature per decade (A). From Ben
Indo-Pacific, warming sea temperatures will favour the Raïs Lasram F. and Mouillot D., 2009
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FUTURE CLIMATE (2070-2099) AND THE PAST CLIMATE (1961-1990)
Model prediction on Sea Surface Temperature variations between 2070-2090 and 1961-1990
Source: Piero Lionello, Università del Salento
Monitoring Marine Invasive Species in Mediterranean MPAs: A strategy and practical guide for managers 17