Page 13 - climate-change2013
P. 13
Projected change by the projections also suggest an increase in the number,
frequency and intensity of extreme warm air and water
end of the century events across the region (see review by Di Carlo and
Otero, 2012).
Most of the models’ outcomes for the different scenar- Precipitation (rain and snow) is expected to decrease in
ios include a rise in air temperature over the Mediter- the Mediterranean area, particularly in summer, when
ranean region by the end of the 21st century. Compari- the risk of drought will be higher. In the A1B scenario,
sons of the projected temperatures with the averages precipitation will decrease by 25% in summer and 10%
for the first half of the 20th century show an increase in winter by 2100, with major variations between the
of 2–5°C for the Mediterranean, with a mean of 3.2°C, southern Mediterranean countries and regions such as
which is higher than the global average (2.6°C). Climate Iberia, Anatolia and the Balkans.
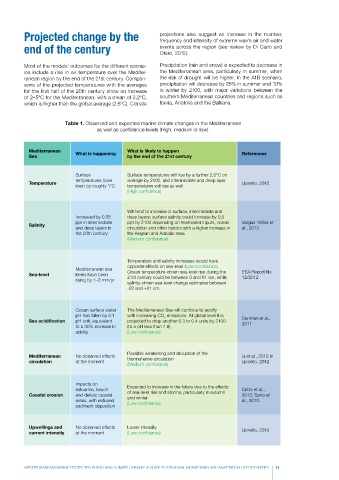
Table 1. Observed and expected marine climate changes in the Mediterranean
as well as confidence levels (High, medium or low).
Mediterranean What is happening What is likely to happen References
Sea by the end of the 21st century
Surface Surface temperatures will rise by a further 2.5°C on
temperatures have average by 2100, and intermediate and deep layer
Temperature Lionello, 2012
risen by roughly 1°C temperatures will rise as well
(High confidence)
Will tend to increase in surface, intermediate and
Increased by 0.05 deep layers; surface salinity could increase by 0.5
ppt in intermediate ppt by 2100 depending on freshwater inputs, ocean Vargas-Yáñez et
Salinity
and deep layers in circulation and other factors with a higher increase in al., 2012
the 20th century the Aegean and Adriatic seas
(Medium confidence)
Temperature and salinity increases would have
opposite effects on sea-level (Low confidence).
Mediterranean sea
Sea-level levels have been Ocean temperature-driven sea-level rise during the EEA Report No
21st century could be between 3 and 61 cm, while
12/2012
rising by 1–3 mm/yr
salinity-driven sea-level change estimates between
-22 and +31 cm.
Ocean surface water The Mediterranean Sea will continue to acidify
pH has fallen by 0.1 with increasing CO emissions. At global level it is
2
Sea acidification pH unit, equivalent projected to drop another 0.3 to 0.4 units by 2100 Denman et al.,
to a 30% increase in (to a pH less than 7.8) 2011
acidity (Low confidence)
Possible weakening and disruption of the
Mediterranean No observed effects thermohaline circulation Li et al., 2012 in
circulation at the moment Lionello, 2012
(Medium confidence)
Impacts on Expected to increase in the future due to the effects
estuarine, beach Critto et al.,
Coastal erosion and deltaic coastal of sea-level rise and storms, particularly in autumn 2012; Sano et
and winter
areas, with reduced (Low confidence) al., 2010.
sediment deposition
Upwellings and No observed effects Lower intensity Lionello, 2012
current intensity at the moment (Low confidence)
MEDITERRANEAN MARINE PROTECTED AREAS AND CLIMATE CHANGE: A GUIDE TO REGIONAL MONITORING AND ADAPTATION OPPORTUNITIES 11