Page 7 - Bracciali_2016
P. 7
122 C. Bracciali et al. / Marine Environmental Research 113 (2016) 116e123
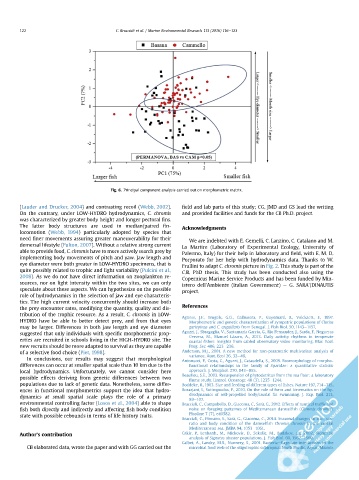
Fig. 6. Principal component analysis carried out on morphometric matrix.
(Lauder and Drucker, 2004) and contrasting recoil (Webb, 2002). field and lab parts of this study; CG, JMD and GS lead the writing
On the contrary, under LOW-HYDRO hydrodynamics, C. chromis and provided facilities and funds for the CB Ph.D. project.
was characterized by greater body height and longer pectoral fins.
The latter body structures are used in median/paired fin- Acknowledgments
locomotion (Webb, 1994) particularly adopted by species that
need finer movements assuring greater maneuverability for their We are indebted with E. Gemelli, C. Lanzino, C. Catalano and M.
demersal lifestyle (Fulton, 2007). Without a relative strong current Lo Martire (Laboratory of Experimental Ecology, University of
able to provide food, C. chromis have to more actively search prey by Palermo, Italy) for their help in laboratory and field, with E. M. D.
implementing body movements of pitch and yaw. Jaw length and Porporato for her help with hydrodynamics data. Thanks to W.
eye diameter were both greater in LOW-HYDRO specimens, that is Frullini to adapt C. chromis picture in Fig. 2. This study is part of the
quite possibly related to trophic and light variability (Pulcini et al., C.B. PhD thesis. This study has been conducted also using the
2008). As we do not have direct information on zooplankton re- Copernicus Marine Service Products and has been funded by Min-
sources, nor on light intensity within the two sites, we can only
istero dell'Ambiente (Italian Government) e G. SARA'/DINAUTIS
speculate about these aspects. We can hypothesize on the possible project.
role of hydrodynamics in the selection of jaw and eye characteris-
tics. The high current velocity concurrently should increase both
the prey encounter rates, modifying the quantity, quality and dis- References
tribution of the trophic resource. As a result, C. chromis in LOW-
Agnese, J.F., Teugels, G.G., Galbusera, P., Guyomard, R., Volckaert, F., 1997.
HYDRO have be able to better detect prey, and from that eyes Morphometric and genetic characterization of sympatric populations of Clarias
may be larger. Differences in both jaw length and eye diameter gariepinus and C. anguillaris from Senegal. J. Fish Biol. 50, 1143e1157.
suggested that only individuals with specific morphometric prop- Aguzzi, J., Sbragaglia, V., Santamaria Garcia, G., Río Fernandez, J., Sarda, F., Nogueras
Cervera, M., Manuel L azaro, A., 2013. Daily activity rhythms in temperate
erties are recruited in schools living in the HIGH-HYDRO site. The coastal fishes: insights from cabled observatory video monitoring. Mar. Ecol.
new recruits should be more adapted to survival as they are capable Prog. Ser. 486, 223e236.
of a selective food choice (Piet, 1998). Anderson, M.J., 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of
variance. Aust. Ecol 26, 32e46.
In conclusions, our results may suggest that morphological
Antonucci, F., Costa, C., Aguzzi, J., Cataudella, S., 2009. Ecomorphology of morpho-
differences can occur at smaller spatial scale than 10 km due to the functional relationships in the family of Sparidae: a quantitative statistic
local hydrodynamics. Unfortunately, we cannot consider here approach. J. Morphol. 270, 843e855.
Beaulieu, S.E., 2003. Resuspension of phytodetritus from the sea floor: a laboratory
possible effects deriving from genetic differences between two
flume study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 48 (3), 1235e1244.
populations due to lack of genetic data. Nonetheless, some differ- Boddeke, R., 1963. Size and feeding of different types of fishes. Nature 197, 714e715.
ences in functional morphometrics support the idea that hydro- Borazjani, I., Sotiropoulos, F., 2010. On the role of form and kinematics on the hy-
drodynamics of self-propelled body/caudal fin swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 213,
dynamics at small spatial scale plays the role of a primary
89e107.
environmental controlling factor (Losos et al., 2004) able to shape Bracciali, C., Campobello, D., Giacoma, C., Sar a, G., 2012. Effects of nautical traffic and
fish both directly and indirectly and affecting fish body condition noise on foraging patternes of Mediterranean damselfish (Chromis chromis).
PlosOne 7 (7), e40582.
state with possible rebounds in terms of life history traits.
Bracciali, C., Piovano, S., Sar a, G., Giacoma, C., 2014. Seasonal changes in size, sex-
ratio and body condition of the damselfish Chromis chromis in the central
Mediterranean sea. JMBA 94, 1053e1061.
Author's contribution Cakic, P., Lenhardt, M., Mickovic, D., Sekulic, M., Budakov, L.J., 2002. Biometric
analysis of Signatus abaster populations. J. Fish Biol. 60, 1562e1569.
Calbet, A., Landry, M.R., Nunnery, S., 2001. Bacteriaeflagellate interactions in the
CB elaborated data, wrote the paper and with GG carried out the microbial food web of the oligotrophic subtropical North Pacific. Aquat. Microb.