Page 123 - Invasive_Species_2013
P. 123
Mediterranean invasive species factsheet
Similar species the eastern Mediterranean: Syria, Cyprus, the
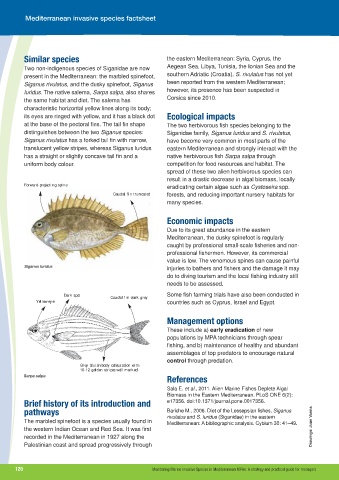
Two non-indigenous species of Siganidae are now Aegean Sea, Libya, Tunisia, the Ionian Sea and the
present in the Mediterranean: the marbled spinefoot, southern Adriatic (Croatia). S. rivulatus has not yet
been reported from the western Mediterranean;
Siganus rivulatus, and the dusky spinefoot, Siganus
however, its presence has been suspected in
luridus. The native salema, Sarpa salpa, also shares
Corsica since 2010.
the same habitat and diet. The salema has
characteristic horizontal yellow lines along its body;
its eyes are ringed with yellow, and it has a black dot Ecological impacts
at the base of the pectoral fins. The tail fin shape The two herbivorous fish species belonging to the
distinguishes between the two Siganus species: Siganidae family, Siganus luridus and S. rivulatus,
Siganus rivulatus has a forked tail fin with narrow, have become very common in most parts of the
translucent yellow stripes, whereas Siganus luridus eastern Mediterranean and strongly interact with the
has a straight or slightly concave tail fin and a native herbivorous fish Sarpa salpa through
uniform body colour. competition for food resources and habitat. The
spread of these two alien herbivorous species can
result in a drastic decrease in algal biomass, locally
Forward-projecting spine
eradicating certain algae such as Cystoseira spp.
Caudal fin truncated forests, and reducing important nursery habitats for
many species.
Economic impacts
Due to its great abundance in the eastern
Mediterranean, the dusky spinefoot is regularly
caught by professional small-scale fisheries and non-
professional fishermen. However, its commercial
value is low. The venomous spines can cause painful
Siganus luridus injuries to bathers and fishers and the damage it may
do to diving tourism and the local fishing industry still
needs to be assessed.
Dark spot Some fish farming trials have also been conducted in
Caudal fin dark grey
Yellow eye countries such as Cyprus, Israel and Egypt.
Management options
These include a) early eradication of new
populations by MPA technicians through spear
fishing, and b) maintenance of healthy and abundant
assemblages of top predators to encourage natural
control through predation.
Grey bluish body colouration with
10-12 golden stripes well marked
Sarpa salpa
References
Sala E. et al., 2011. Alien Marine Fishes Deplete Algal
Biomass in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 6(2):
Brief history of its introduction and e17356. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017356.
pathways Bariche M., 2006. Diet of the Lessepsian fishes, Siganus
rivulatus and S. luridus (Siganidae) in the eastern
The marbled spinefoot is a species usually found in Mediterranean: A bibliographic analysis. Cybium 30: 41–49.
the western Indian Ocean and Red Sea. It was first Drawings: Juan Varela
recorded in the Mediterranean in 1927 along the
Palestinian coast and spread progressively through
120 Monitoring Marine Invasive Species in Mediterranean MPAs: A strategy and practical guide for managers