Page 5 - Stöck_alii_2008
P. 5
BMC Evolutionary Biology 2008, 8:56 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2148/8/56
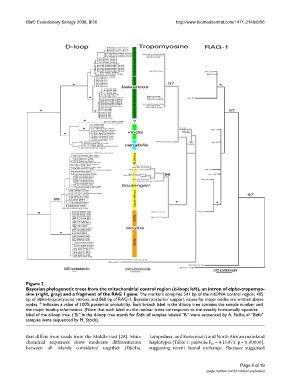
Bayesian phylogenetic trees from the mitochondrial control region (d-loop; left), an intron of alpha-tropomyosine (right, gray) and a fragment of the RAG 1 geneFigure 2
Bayesian phylogenetic trees from the mitochondrial control region (d-loop; left), an intron of alpha-tropomyo-
sine (right, gray) and a fragment of the RAG 1 gene. The markers comprise 541 bp of the mtDNA control region, 405
bp of alpha-tropomyosine introns, and 860 bp of RAG-1; Bayesian posterior support values for major nodes are written above
nodes, * indicates a value of 100% posterior probability. Each branch label in the d-loop tree contains the sample number and
the major locality information. (Note that each label on the nuclear trees corresponds to the exactly horizontally opposite
label of the d-loop tree. ("B." in the d-loop tree stands for Bufo; all samples labeled "B." were sequenced by A. Sicilia; all "Bufo"
samples were sequenced by M. Stöck).
that differs from toads from the Middle East [28]. Mito- Lampedusa, and Kerkennah) and North African mainland
chondrial sequences show moderate differentiation haplotypes (Table 1: pairwise F = 0.16073, p = 0.00000),
ST
between all islands considered together (Djerba, suggesting recent faunal exchange. Fluctuate suggested
Page 5 of 19
(page number not for citation purposes)