Page 7 - Sulli_eall_2012
P. 7
Variability of depositional setting along the north-western Sicily continental shelf (Italy) ... 147
Fig. 6 - General stratigraphic pattern of Pleistocene seismic units buried beneath the continental shelf in the Gulf of Termini (as worked
out from multi-channel seismic profiles.
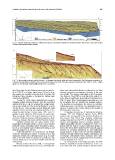
Fig. 7 - High resolution seismic profile (Sparker 1 kJ) showing the seismic units and facies interpreted in the Quaternary succession. In-
terbedded, progradational wedges (LST) are present along the outer shelf; SB: lower sequence boundary of the LQDS; F: fault; s: sliding
plane (see text for more detail; modified from Pepe et al., 2003).
ward they onlap the late Pleistocene erosive unconform- plays even subparallel reflection configuration and thins
ity at 110-130 m of water depth, about 15 km far from seaward generating an apparent truncation in the seis-
the present day coastline along the Gulf of Termini. We mic profiles. This wedge, interpreted as the Transgres-
interpreted these wedges as forming the Falling stage sive Systems Tract (TST) is very thin in the Gulf of Pa-
systems tract (FSST). lermo (Fig. 8) and thicker in the Gulf of Termini Imerese
(Fig. 7) where three backstepping parasequences can
Along the shelf edge progradational wedges be recognized that are bounded by flooding surfaces.
showing oblique parallel horizons form the Lowstand The lowermost parasequence lies above an extensive
systems tract (LST, Fig. 8). Seaward the wedges pinch- submerged wave cut terrace; the uppermost parase-
out at water depth of 150-190 m; the thickness is up to quence is thicker in the sector offshore the mouths of
100 ms (t.w.t.). These wedges formed during the LGM the Imera and Torto River.
lowstand (20-18 ka) and are stacked with the FSST
along the shelf margin. In plain view, FSST and LST A downlap surface (Fig. 7) marking the transition
wedges extend along the shelf margin for several km. between TST and Highstand System Tracts (HST)
They are absent only in the canyon headscars and, in seismic units, corresponds to the maximum flooding sur-
the Gulf of Palermo, along a shelf break segment, about face (sensu Vail, 1987). The overlying sedimentary
5 km long, between the Oreto and the Eleuterio canyon. wedge, interpreted as the HST, is formed by thin, con-
tinuous and aggrading horizons evolving upwards to
Samples coming from the upper portion of the slightly prograding reflectors. Landward this unit is con-
prograding shelf margin wedges reveals coarse grained tinuous with the modern coastal sedimentary wedge. In
bioclastic sands containing benthic foraminifera depos- front of the Imera River mouth the HST deposits appear
ited in a very shallow water environment during a cold involved in creeping interpreted as syn-sedimentary
period (Catalano et al., 2011b). gravity features. In this sector the sea floor instability is
promoted by high sedimentary supply, earthquakes, flu-
At the top both the FSST and the LST are truncat- id seepage. Alternatively these structures were inter-
ed by the transgressive surface of erosion (t.s.e.) that preted as due to waves, hyperpycnal flows and bottom
downslope merge into a drowing surface (Fig. 8). Land- currents (Urgeles et al., 2011).
ward, in the inner shelf, this surface is scoured by a few
incised valleys up to one hundred meters wide and ten As consequence of the wedge geometry, the HST
meters deep. thickness regularly increases landward up to 35 m in
front of the main river mouths. At places seaward exten-
Moving toward the inner shelf, a transgressive
sedimentary wedge lies above the t.s.e.; the wedge dis-