Page 4 - Cocito_alii_2015
P. 4
Research & development
minimising potentially adverse activities. Within this
context, ENEA aims to develop and realize actions for
sustainable tourism. By popularizing marine biological
and environmental special features, knowledge will be
increased thus generating further awareness among
residents and nearby populations and visitors, making
the marine resources more easy to protect against non-
sustainable tourism.
Among the special underwater features of the Egadi
Islands, Posidonia oceanica meadows, included in
the Habitat Directive (43/92/CEE), are one of the
most important biocoenoses for their abundance and
distribution all around the shallow seabed of the islands
(~7.700 ha). In addition, on the deep rocky outcrops
and shoals, the coralligenous community represents a
Mediterranean habitat of high ecological importance.
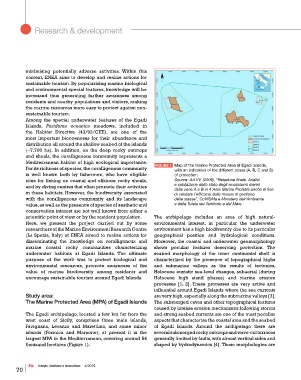
For its richness of species, the coralligenous community FIGURE 1 Map of the Marine Protected Area of Egadi Islands,
with an indication of the different zones (A, B, C and D)
is well known both by fishermen, who have eligible of protection
sites for fishing on coastal and offshore rocky shoals, Source: AA.VV. (2009), “Relazione finale. Analisi
and by diving centres that often promote their activities e valutazione dello stato degli ecosistemi marini
in these habitats. However, the biodiversity associated delle zone A e B in 4 Aree Marine Protette anche al fine
di valutare l’efficacia delle misure di gestione
with the coralligenous community and its landscape delle stesse”, CoNISMa e Ministero dell’Ambiente
value, as well as the presence of species of aesthetic and e della Tutela del Territorio e del Mare
conservation interest are not well known from either a
scientific point of view or by the resident population. The archipelago includes an area of high natural-
Here, we present the project carried out by some environmental interest, in particular the underwater
researchers of the Marine Environment Research Centre environment has a high biodiversity due to its particular
(La Spezia, Italy) of ENEA aimed to realize actions for geographical position and hydrological conditions.
disseminating the knowledge on coralligenous and Moreover, the coastal and underwater geomorphology
marine coastal rocky communities characterizing shows peculiar features deserving protection. The
underwater habitats at Egadi Islands. The ultimate seabed morphology of the inner continental shelf is
purpose of the work was to protect biological and characterized by the presence of topographical highs
environmental resources, promote awareness of the and submarine valleys as the results of tectonics,
value of marine biodiversity among residents and Holocene eustatic sea-level changes, subaerial (during
encourage sustainable tourism around Egadi Islands. Holocene high stand phases) and marine erosion
processes [1, 2]. These processes are very active and
influential around Egadi Islands where the sea currents
Study area: are very high, especially along the submarine valleys [3].
The Marine Protected Area (MPA) of Egadi Islands The submerged caves and other topographical features
caused by intense erosion mechanisms following storms
The Egadi archipelago, located a few km far from the and strong seabed currents are one of the most peculiar
west coast of Sicily, comprises three main islands, aspects that characterise the coastal area and the seabed
Favignana, Levanzo and Marettimo, and some minor of Egadi Islands. Around the archipelago there are
islands (Formica and Maraone); at present it is the several submerged rocky outcrops and wave-cut terraces
largest MPA in the Mediterranean, covering around 54 generally limited by faults, with almost vertical sides and
thousand hectares (Figure 1). shaped by hydrodynamics [4]. Those morphologies are
EAI Energia, Ambiente e Innovazione 4/2015
70