Page 91 - Invasive_Species_2013
P. 91
Mediterranean invasive species factsheet
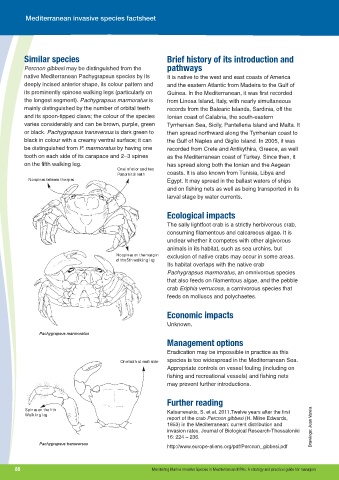
Similar species Brief history of its introduction and
Percnon gibbesi may be distinguished from the pathways
native Mediterranean Pachygrapsus species by its It is native to the west and east coasts of America
deeply incised anterior shape, its colour pattern and and the eastern Atlantic from Madeira to the Gulf of
its prominently spinose walking legs (particularly on Guinea. In the Mediterranean, it was first recorded
the longest segment). Pachygrapsus marmoratus is from Linosa Island, Italy, with nearly simultaneous
mainly distinguished by the number of orbital teeth records from the Balearic Islands, Sardinia, off the
and its spoon-tipped claws; the colour of the species Ionian coast of Calabria, the south-eastern
varies considerably and can be brown, purple, green Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicily, Pantelleria Island and Malta. It
or black. Pachygrapsus transversus is dark green to then spread northward along the Tyrrhenian coast to
black in colour with a creamy ventral surface; it can the Gulf of Naples and Giglio Island. In 2005, it was
be distinguished from P. marmoratus by having one recorded from Crete and Antikythira, Greece, as well
tooth on each side of its carapace and 2–3 spines as the Mediterranean coast of Turkey. Since then, it
on the fifth walking leg. has spread along both the Ionian and the Aegean
One inferior and two
Postorbital teeth coasts. It is also known from Tunisia, Libya and
No spines between the eyes Egypt. It may spread in the ballast waters of ships
and on fishing nets as well as being transported in its
larval stage by water currents.
Ecological impacts
The sally lightfoot crab is a strictly herbivorous crab,
consuming filamentous and calcareous algae. It is
unclear whether it competes with other algivorous
animals in its habitat, such as sea urchins, but
No spines on the margin exclusion of native crabs may occur in some areas.
of the 5th walking leg
Its habitat overlaps with the native crab
Pachygrapsus marmoratus, an omnivorous species
that also feeds on filamentous algae, and the pebble
crab Eriphia verrucosa, a carnivorous species that
feeds on molluscs and polychaetes.
Economic impacts
Unknown.
Pachygrapsus marmoratus
Management options
Eradication may be impossible in practice as this
One tooth at each side species is too widespread in the Mediterranean Sea.
Appropriate controls on vessel fouling (including on
fishing and recreational vessels) and fishing nets
may prevent further introductions.
Further reading
Spines on the fith Katsanevakis, S. et al. 2011.Twelve years after the first
Walking leg
report of the crab Percnon gibbesi (H. Milne Edwards,
1853) in the Mediterranean: current distribution and Drawings: Juan Varela
invasion rates. Journal of Biological Research-Thessaloniki
16: 224 – 236.
Pachygrapsus transversus
http://www.europe-aliens.org/pdf/Percnon_gibbesi.pdf
88 Monitoring Marine Invasive Species in Mediterranean MPAs: A strategy and practical guide for managers