Page 40 - Lo Cascio_2015
P. 40
568 PIETRO LO CASCIO
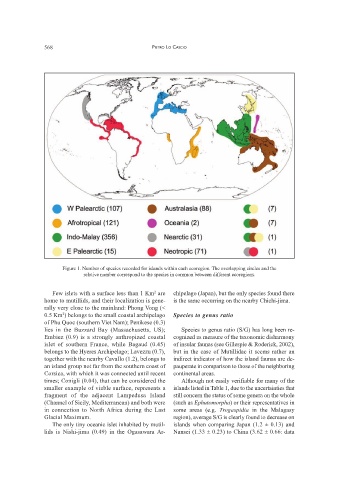
Figure 1. Number of species recorded for islands within each ecoregion. The overlapping circles and the
relative number correspond to the species in common between different ecoregions.
Few islets with a surface less than 1 Km are chipelago (Japan), but the only species found there
2
home to mutillids, and their localization is gene- is the same occurring on the nearby Chichi-jima.
rally very close to the mainland: Phong Vong (<
0.5 Km ) belongs to the small coastal archipelago Species to genus ratio
2
of Phu Quoc (southern Viet Nam); Penikese (0.3)
lies in the Buzzard Bay (Massachusetts, US); Species to genus ratio (S/G) has long been re-
Embiez (0.9) is a strongly anthropized coastal cognized as measure of the taxonomic disharmony
islet of southern France, while Bagaud (0.45) of insular faunas (see Gillespie & Roderick, 2002),
belongs to the Hyeres Archipelago; Lavezzu (0.7), but in the case of Mutillidae it seems rather an
together with the nearby Cavallo (1.2), belongs to indirect indicator of how the island faunas are de-
an island group not far from the southern coast of pauperate in comparison to those of the neighboring
Corsica, with which it was connected until recent continental areas.
times; Conigli (0.04), that can be considered the Although not easily verifiable for many of the
smaller example of viable surface, represents a islands listed in Table 1, due to the uncertainties that
fragment of the adjacent Lampedusa Island still concern the status of some genera on the whole
(Channel of Sicily, Mediterranean) and both were (such as Ephutomorpha) or their representatives in
in connection to North Africa during the Last some areas (e.g. Trogaspidia in the Malagasy
Glacial Maximum. region), average S/G is clearly found to decrease on
The only tiny oceanic islet inhabited by mutil- islands when comparing Japan (1.2 ± 0.13) and
lids is Nishi-jima (0.49) in the Ogasawara Ar- Nansei (1.33 ± 0.23) to China (3.62 ± 0.66: data