Page 4 - Falconi_et_al_2017
P. 4
Landslide Monitoring at the Cala Rossa … 125
Table 1 Geotechnical characters
Features Units of measurement Value
of calcarenites
Specific gravity (Gs) g/cm 3 2.7
SiO 2 content % <1
MgCa(CO 3 ) 2 content % 1–3
Average grain size mm 0.3
Total porosity (n) % 40–50
Compressive strength (r) kg/cm 2 20–30
tectonic activity involves Tyrrhenian sediments and more the measured joints were plotted using the “Georient open
recentcontinentaldeposits,asrevealedbykinematicindicators source software” and the Schmidt equi-areal stereographic
of NW-SE, NE-SW and W-E strike-slip faults (Incandela projection (lower hemisphere). Furthermore, the mechanical
1996) and of differential uplift (Antonioli et al. 2006). features of the rock mass, including the mineralogical
The study is focused on the bay named “Cala Rossa”, characteristics and the rock compressive strength, were
located in the eastern side of the island (Fig. 1), where the assessed with field instruments (Schmidt Hammer sclerom-
Pleistocene biocalcarenites form some cliffs with height eter) and laboratory experiments (thin sections and point
ranging from few meters up to over 30 m. This area is load test). On the basis of the geological and geomechanical
classified as high and very high landslide hazard zone features, the values of Beniawsky/Romana (RMR/SMR) and
(Regione Siciliana 2006). Sicily Region classifications (Regione Siciliana 2013b) were
The cliffs of Cala Rossa are separated from the sea by a assigned to each station. The latter proposes a simplified
narrow strip of talus deposits, assuming the shape of a sea- approach generating an aggregate of some geomorphologi-
sonal sea cliffs (Martino and Mazzanti 2014). In the west cal, environmental and historical parameters with the
side of Cala Rossa, the stiff rock slab lies on the ductile clays mechanical characteristics typical of the traditional
belonging to the Pliocene formation. The contact between classification.
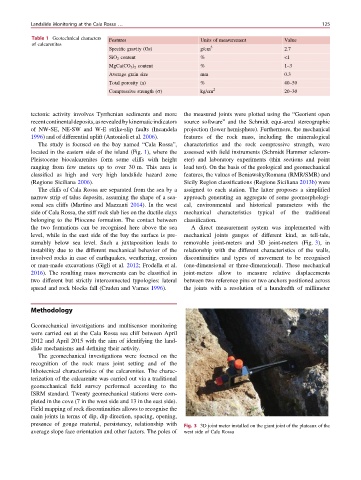
the two formations can be recognised here above the sea A direct measurement system was implemented with
level, while in the east side of the bay the surface is pre- mechanical joints gauges of different kind, as tell-tale,
sumably below sea level. Such a juxtaposition leads to removable joint-meters and 3D joint-meters (Fig. 3), in
instability due to the different mechanical behavior of the relationship with the different characteristics of the walls,
involved rocks in case of earthquakes, weathering, erosion discontinuities and types of movement to be recognised
or man-made excavations (Gigli et al. 2012; Frodella et al. (one-dimensional or three-dimensional). These mechanical
2016). The resulting mass movements can be classified in joint-meters allow to measure relative displacements
two different but strictly interconnected typologies: lateral between two reference pins or two anchors positioned across
spread and rock blocks fall (Cruden and Varnes 1996). the joints with a resolution of a hundredth of millimeter
Methodology
Geomechanical investigations and multisensor monitoring
were carried out at the Cala Rossa sea cliff between April
2012 and April 2015 with the aim of identifying the land-
slide mechanisms and defining their activity.
The geomechanical investigations were focused on the
recognition of the rock mass joint setting and of the
lithotecnical characteristics of the calcarenites. The charac-
terization of the calcarenite was carried out via a traditional
geomechanical field survey performed according to the
ISRM standard. Twenty geomechanical stations were com-
pleted in the cove (7 in the west side and 13 in the east side).
Field mapping of rock discontinuities allows to recognise the
main joints in terms of dip, dip direction, spacing, opening,
presence of gouge material, persistency, relationship with Fig. 3 3D joint meter installed on the giant joint of the plateaux of the
average slope face orientation and other factors. The poles of west side of Cala Rossa