Page 7 - Falconi_et_al_2017
P. 7
128 L. Falconi et al.
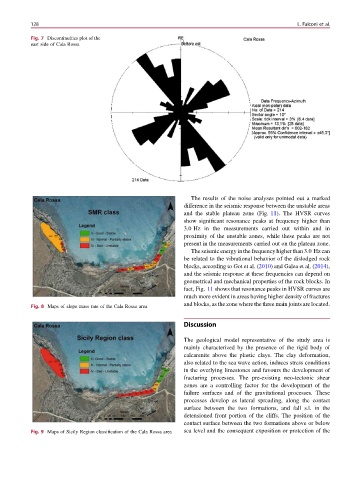
Fig. 7 Discontinuities plot of the
east side of Cala Rossa
The results of the noise analyses pointed out a marked
difference in the seismic response between the unstable areas
and the stable plateau zone (Fig. 11). The HVSR curves
show significant resonance peaks at frequency higher than
3.0 Hz in the measurements carried out within and in
proximity of the unstable zones, while these peaks are not
present in the measurements carried out on the plateau zone.
The seismic energy in the frequency higher than 3.0 Hz can
be related to the vibrational behavior of the dislodged rock
blocks, according to Got et al. (2010) and Galea et al. (2014),
and the seismic response at these frequencies can depend on
geometrical and mechanical properties of the rock blocks. In
fact, Fig. 11 shows that resonance peaks in HVSR curves are
much more evident in areas having higher density of fractures
and blocks, as the zone where the three main joints are located.
Fig. 8 Maps of slope mass rate of the Cala Rossa area
Discussion
The geological model representative of the study area is
mainly characterized by the presence of the rigid body of
calcarenite above the plastic clays. The clay deformation,
also related to the sea wave action, induces stress conditions
in the overlying limestones and favours the development of
fracturing processes. The pre-existing neo-tectonic shear
zones are a controlling factor for the development of the
failure surfaces and of the gravitational processes. These
processes develop as lateral spreading, along the contact
surface between the two formations, and fall s.l. in the
detensioned front portion of the cliffs. The position of the
contact surface between the two formations above or below
Fig. 9 Maps of Sicily Region classification of the Cala Rossa area sea level and the consequent exposition or protection of the