Page 8 - Falconi_et_al_2017
P. 8
Landslide Monitoring at the Cala Rossa … 129
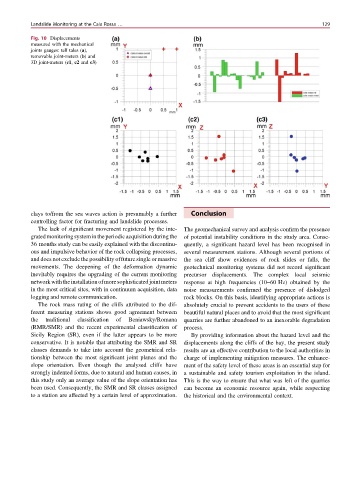
Fig. 10 Displacements
measured with the mechanical
joints gauges: tell tales (a),
removable joint-meters (b) and
3D joint-meters (c1, c2 and c3)
clays to/from the sea waves action is presumably a further Conclusion
controlling factor for fracturing and landslide processes.
The lack of significant movement registered by the inte- The geomechanical survey and analysis confirm the presence
gratedmonitoringsystemintheperiodicacquisitionduringthe of potential instability conditions in the study area. Conse-
36 months study can be easily explained with the discontinu- quently, a significant hazard level has been recognised in
ous and impulsive behavior of the rock collapsing processes, several measurement stations. Although several portions of
and does not exclude the possibility offuture single or massive the sea cliff show evidences of rock slides or falls, the
movements. The deepening of the deformation dynamic geotechnical monitoring systems did not record significant
inevitably requires the upgrading of the current monitoring precursor displacements. The complex local seismic
networkwiththeinstallationofmoresophisticatedjointmeters response at high frequencies (10–60 Hz) obtained by the
in the most critical sites, with in continuum acquisition, data noise measurements confirmed the presence of dislodged
logging and remote communication. rock blocks. On this basis, identifying appropriate actions is
The rock mass rating of the cliffs attributed to the dif- absolutely crucial to prevent accidents to the users of these
ferent measuring stations shows good agreement between beautiful natural places and to avoid that the most significant
the traditional classification of Beniawsky/Romana quarries are further abandoned to an inexorable degradation
(RMR/SMR) and the recent experimental classification of process.
Sicily Region (SR), even if the latter appears to be more By providing information about the hazard level and the
conservative. It is notable that attributing the SMR and SR displacements along the cliffs of the bay, the present study
classes demands to take into account the geometrical rela- results are an effective contribution to the local authorities in
tionship between the most significant joint planes and the charge of implementing mitigation measures. The enhance-
slope orientation. Even though the analysed cliffs have ment of the safety level of these areas is an essential step for
strongly indented forms, due to natural and human causes, in a sustainable and safety tourism exploitation in the island.
this study only an average value of the slope orientation has This is the way to ensure that what was left of the quarries
been used. Consequently, the SMR and SR classes assigned can become an economic resource again, while respecting
to a station are affected by a certain level of approximation. the historical and the environmental context.