Page 4 - Brain_morphology_2008
P. 4
G. Palmieri et al.
laterally and forms a 90° angle at about 200 µm
from its rostral end, thus giving rise to the preopti-
cus part of the nucleus preopticus-periventricularis
(the nucleus preopticus itself) (Figure 2).The pre-
opticus component of the nucleus extends aborally
for about 700 µm and, beyond its caudal end, the
periventricularis nucleus can still be observed for
about 120-150 µm. This most caudal end of the
nucleus periventricularis borders only with the dor-
sal wall of the ventricle. As a whole, the nucleus
preopticus-periventricularis is L-shaped; its vertical
component being represented by the nucleus
periventricularis and its horizontal one by the
nucleus preopticus which owes its name to the fact
that it is placed dorsally to the optic chiasm.
The nucleus preopticus-periventricularis is made
up of multipolar neurons whose perikaryon is usu-
ally ellipsoidal in shape (Figure 2).There exist two
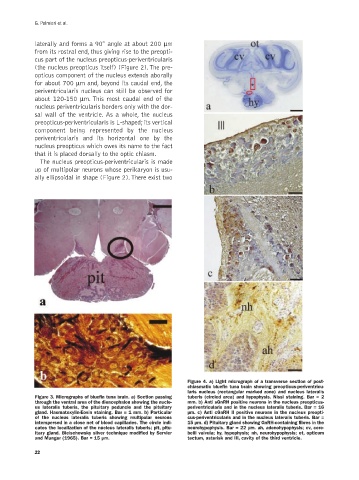
Figure 4. a) Light micrograph of a transverse section of post-
chiasmatic bluefin tuna brain showing preopticus-periventricu-
laris nucleus (rectangular marked zone) and nucleus lateralis
Figure 3. Micrographs of bluefin tuna brain. a) Section passing tuberis (circled area) and hypophysis. Nissl staining. Bar = 2
through the ventral area of the diencephalon showing the nucle- mm. b) Anti sGnRH positive neurons in the nucleus preopticus-
us lateralis tuberis, the pituitary peduncle and the pituitary periventricularis and in the nucleus lateralis tuberis. Bar = 16
gland. Haematoxylin-Eosin staining. Bar = 1 mm. b) Particular µm. c) Anti cGnRH II positive neurons in the nucleus preopti-
of the nucleus lateralis tuberis showing multipolar neurons cus-periventricularis and in the nucleus lateralis tuberis. Bar =
interspersed in a close net of blood capillaries. The circle indi- 15 µm. d) Pituitary gland showing GnRH-containing fibres in the
cates the localization of the nucleus lateralis tuberis; pit, pitu- neurohypophysis. Bar = 22 µm. ah, adenohypophysis; cv, cere-
itary gland. Bielschowsky silver technique modified by Servier belli valvula; hy, hypophysis; nh, neurohypophysis; ot, opticum
and Munger (1965). Bar = 15 µm. tectum, asterisk and III, cavity of the third ventricle.
22