Page 6 - MedSens_index_2021
P. 6
Ecological Indicators 122 (2021) 107296
E. Turicchia et al.
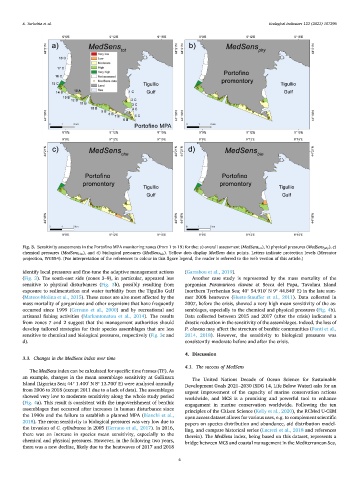
Fig. 3. Sensitivity assessments in the Portofino MPA monitoring zones (from 1 to 19) for the: a) overall assessment (MedSens tot ), b) physical pressures (MedSens phy ), c)
chemical pressures (MedSens che ), and d) biological pressures (MedSens bio ). Yellow dots display MedSens data points. Letters indicate protection levels (Mercator
projection, WGS84). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
identify local pressures and fine-tune the adaptive management actions (Garrabou et al., 2019).
(Fig. 3). The south-east side (zones 3–9), in particular, appeared less Another case study is represented by the mass mortality of the
sensitive to physical disturbances (Fig. 3b), possibly resulting from gorgonian Paramuricea clavata at Secca del Papa, Tavolara Island
′
◦
◦
′
exposure to sedimentation and water turbidity from the Tigullio Gulf (northern Tyrrhenian Sea; 40 54.910 N 9 44.840 E) in the late sum-
(Mateos-Molina et al., 2015). These zones are also most affected by the mer 2008 heatwave (Huete-Stauffer et al., 2011). Data collected in
mass mortality of gorgonians and other organisms that have frequently 2007, before the crisis, showed a very high mean sensitivity of the as-
occurred since 1999 (Cerrano et al., 2000) and by recreational and semblages, especially to the chemical and physical pressures (Fig. 4b).
artisanal fishing activities (Markantonatou et al., 2014). The results Data collected between 2015 and 2017 (after the crisis) indicated a
from zones 7 and 2 suggest that the management authorities should drastic reduction in the sensitivity of the assemblages. Indeed, the loss of
develop tailored strategies for their species assemblages that are less P. clavata may affect the structure of benthic communities (Ponti et al.,
sensitive to chemical and biological pressures, respectively (Fig. 3c and 2014, 2018). However, the sensitivity to biological pressures was
d). consistently moderate before and after the crisis.
4. Discussion
3.3. Changes in the MedSens index over time
4.1. The success of MedSens
The MedSens index can be calculated for specific time frames (TF). As
an example, changes in the mean assemblage sensitivity at Gallinara The United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable
◦
′
′
◦
Island (Ligurian Sea; 44 1.400 N 8 13.700 E) were analysed annually
Development Goals 2021–2030 (SDG 14, Life Below Water) asks for an
from 2006 to 2018 (except 2011 due to a lack of data). The assemblages
urgent improvement of the capacity of marine conservation actions
showed very low to moderate sensitivity along the whole study period worldwide, and MCS is a promising and powerful tool to enhance
(Fig. 4a). This result is consistent with the impoverishment of benthic
engagement in marine conservation worldwide. Following the ten
assemblages that occurred after increases in human disturbance since principles of the Citizen Science (Kelly et al., 2020), the RCMed U-CEM
the 1990s and the failure to establish a planned MPA (Bianchi et al.,
open access dataset allows for various uses, e.g. to complement scientific
2018). The mean sensitivity to biological pressures was very low due to papers on species distribution and abundance, aid distribution model-
the invasion of C. cylindracea in 2005 (Cerrano et al., 2017). In 2016,
ling, and compare historical series (Lucrezi et al., 2018 and references
there was an increase in species mean sensitivity, especially to the therein). The MedSens index, being based on this dataset, represents a
chemical and physical pressures. However, in the following two years,
bridge between MCS and coastal management in the Mediterranean Sea,
there was a new decline, likely due to the heatwaves of 2017 and 2018
6