Page 18 - Water-energy_2020
P. 18
F. Calise, et al. Energy Conversion and Management 220 (2020) 113043
Fig. 12. Proposed System 2 (PS2). Summer day, main electrical fluxes.
•
6. Conclusion during summer, the global efficiency of the concentrating photo-
voltaic and thermal field is satisfying, and the solar production
This work presented the dynamic simulations of two solar poly- covers a significant amount of the total energy demand, due to the
generation plants, consisted of thermally- and electrically-driven tech- high beam radiation;
nologies for the production of freshwater, space heating and cooling, • during winter, and due to the decrease of thermal and electrical
domestic hot water, and electricity. In particular, the first layout was efficiency of the concentrating photovoltaic and thermal collectors,
based on concentrating photovoltaic and thermal collectors, an ab- the energy demand is almost totally covered by auxiliary heaters,
sorption chiller, and a multi effect distillation unit. The second layout mainly activated for the production of freshwater by the multi-effect
was based on photovoltaic panels, heat pumps for space heating/ distillation process and the district space heating;
cooling and domestic hot water, and a reverse osmosis unit. The in- • the obtained primary energy savings, avoided CO 2 emissions, and
vestigated plants were modelled in TRNSYS and their energy, en- simple payback period were equal to 32.2%, 27.8% and 12 years,
vironmental and economic performance were evaluated. The two plants respectively;
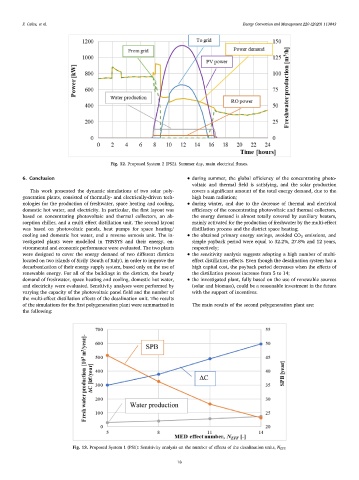
were designed to cover the energy demand of two different districts • the sensitivity analysis suggests adopting a high number of multi-
located on two islands of Sicily (South of Italy), in order to improve the effect distillation effects. Even though the desalination system has a
decarbonization of their energy supply system, based only on the use of high capital cost, the payback period decreases when the effects of
renewable energy. For all of the buildings in the districts, the hourly the distillation process increase from 5 to 14;
demand of freshwater, space heating and cooling, domestic hot water, • the investigated plant, fully based on the use of renewable sources
and electricity were evaluated. Sensitivity analyses were performed by (solar and biomass), could be a reasonable investment in the future
varying the capacity of the photovoltaic panel field and the number of with the support of incentives.
the multi-effect distillation effects of the desalination unit. The results
of the simulations for the first polygeneration plant were summarized in The main results of the second polygeneration plant are:
the following:
Fig. 13. Proposed System 1 (PS1): Sensitivity analysis on the number of effects of the desalination units, N EFF.
18