Page 3 - Geomorphological_2020
P. 3
JOURNAL OF MAPS 3
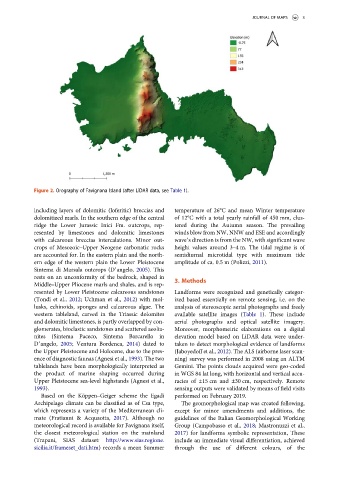
Figure 2. Orography of Favignana Island (after LiDAR data, see Table 1).
including layers of dolomitic (loferitic) breccias and temperature of 26°C and mean Winter temperature
dolomitized marls. In the southern edge of the central of 12°C with a total yearly rainfall of 450 mm, clus-
ridge the Lower Jurassic Inici Fm. outcrops, rep- tered during the Autumn season. The prevailing
resented by limestones and dolomitic limestones winds blow from NW, NNW and ESE and accordingly
with calcareous breccias intercalations. Minor out- wave’s direction is from the NW, with significant wave
crops of Mesozoic–Upper Neogene carbonatic rocks height values around 3–4 m. The tidal regime is of
are accounted for. In the eastern plain and the north- semidiurnal microtidal type with maximum tide
ern edge of the western plain the Lower Pleistocene amplitude of ca. 0.5 m (Polizzi, 2011).
Sintema di Marsala outcrops (D’angelo, 2005). This
rests on an unconformity of the bedrock, shaped in
3. Methods
Middle–Upper Pliocene marls and shales, and is rep-
resented by Lower Pleistocene calcareous sandstones Landforms were recognized and genetically categor-
(Tondi et al., 2012; Uchman et al., 2012) with mol- ized based essentially on remote sensing, i.e. on the
lusks, echinoids, sponges and calcareous algae. The analysis of stereoscopic aerial photographs and freely
western tableland, carved in the Triassic dolomites available satellite images (Table 1). These include
and dolomitic limestones, is partly overlapped by con- aerial photographs and optical satellite imagery.
glomerates, bioclastic sandstones and scattered aeolia- Moreover, morphometric elaborations on a digital
nites (Sintema Paceco, Sintema Barcarello in elevation model based on LiDAR data were under-
D’angelo, 2005; Ventura Bordenca, 2014) dated to taken to detect morphological evidence of landforms
the Upper Pleistocene and Holocene, due to the pres- (Jaboyedoff et al., 2012). The ALS (airborne laser scan-
ence of diagnostic faunas (Agnesi et al., 1993). The two ning) survey was performed in 2008 using an ALTM
tablelands have been morphologically interpreted as Gemini. The points clouds acquired were geo-coded
the product of marine shaping occurred during in WGS 84 lat long, with horizontal and vertical accu-
Upper Pleistocene sea-level highstands (Agnesi et al., racies of ±15 cm and ±30 cm, respectively. Remote
1993). sensing outputs were validated by means of field visits
Based on the Köppen–Geiger scheme the Egadi performed on February 2019.
Archipelago climate can be classified as of Csa type, The geomorphological map was created following,
which represents a variety of the Mediterranean cli- except for minor amendments and additions, the
mate (Fratianni & Acquaotta, 2017). Although no guidelines of the Italian Geomorphological Working
meteorological record is available for Favignana itself, Group (Campobasso et al., 2018; Mastronuzzi et al.,
the closest meteorological station on the mainland 2017) for landforms symbolic representation, These
(Trapani, SIAS dataset: http://www.sias.regione. include an immediate visual differentiation, achieved
sicilia.it/frameset_dati.htm) records a mean Summer through the use of different colours, of the