Page 4 - Marrone_alii_2013
P. 4
Author's personal copy
Zoomorphology
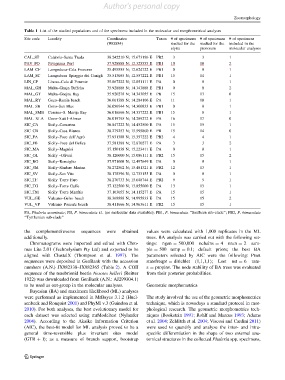
Table 1 List of the studied populations and of the specimens included in the molecular and morphometrical analyses
Site code Locality Coordinates Taxon # of specimens # of specimens # of specimens
(WGS84) studied for the studied for the included in the
elytra pronotum molecular analyses
CAL_ST Calabria–Santa Trada 38.242210 N; 15.673196 E PB2 3 3 1
FAV_PO Favignana–Port 37.928888 N; 12.325555 E PB1 10 10 2
LAM_CF Lampedusa–Cala Francese 35.495555 N; 12.624722 E PB1 0 0 1
LAM_SC Lampedusa–Spiaggia dei Conigli 35.513055 N; 12.557222 E PB1 15 14 1
LIN_CP Linosa–Cala di Ponente 35.867222 N; 12.851111 E PA 0 0 1
MAL_GH Malta–Ghajn Tuffeha 35.928888 N; 14.343888 E PB1 0 0 2
MAL_GT Malta–Gnejna Bay 35.920278 N; 14.343055 E PB 15 13 0
MAL_RY Gozo–Ramla beach 36.061388 N; 14.284166 E PA 11 10 1
MAL_SB Gozo–San Blas 36.056944 N; 14.300833 E PB1 0 0 1
MAL_SMB Comino–S. Marija Bay 36.016666 N; 14.337222 E PB1 15 8 1
MAL_XLA Gozo–Xatt l-Ahmar 36.019795 N; 14.289272 E PA 16 17 0
SIC_CA Sicily–Camarina 36.847222 N; 14.452500 E PA 15 15 1
SIC_CB Sicily–Casa Bianca 38.279253 N; 15.595860 E PB 15 14 0
SIC_FA Sicily–Foce dell’Agro ` 37.931388 N; 15.357222 E PB2 4 4 1
SIC_FB Sicily–Foce del Belice 37.581388 N; 12.870277 E PA 3 3 2
SIC_MA Sicily–Magnisi 37.150138 N; 15.223411 E PA 0 0 1
SIC_OL Sicily –Oliveri 38.120000 N; 15.086111 E PB2 15 15 2
SIC_RO Sicily–Ronciglio 37.971008 N; 12.497649 E PA 0 0 1
SIC_SM Sicily–Sindaro Marina 38.272562 N; 15.481321 E PB2 12 13 1
SIC_SV Sicily–San Vito 38.178396 N; 12.733155 E PA 0 0 1
SIC_TF Sicily–Torre Faro 38.270733 N; 15.648744 E PB2 9 9 1
SIC_TG Sicily–Torre Gaffe 37.122500 N; 13.855000 E PA 13 13 1
SIC_TM Sicily–Torre Manfria 37.103055 N; 14.115277 E PA 15 15 1
VUL_GE Vulcano–Gelso beach 38.368888 N; 14.995833 E PA 15 15 2
VUL_VP Vulcano–Ponente beach 38.411666 N; 14.963611 E PB2 15 15 1
PA, Phaleria acuminata; PB, P. bimaculata s.l. (no molecular data available); PB1, P. bimaculata ‘‘Southern sub-clade’’; PB2, P. bimaculata
‘‘Tyrrhenian sub-clade’’
the complement/reverse sequences were obtained values were calculated with 1,000 replicates in the ML
additionally. trees. BA analysis was carried out with the following set-
Chromatograms were imported and edited with Chro- tings: ngen = 500,000 nchains = 4 nrun = 2 sam-
mas Lite 2.01 (Technelysium Pty Ltd) and exported to be ple = 500 temp = 0.1; default priors; the best BA
aligned with ClustalX (Thompson et al. 1997). The parameters selected by AIC were the following: Prset
sequences were deposited in GenBank with the accession statefreqpr = dirichlet (1,1,1,1); Lset nst = 6 rate-
numbers (A.N.) JX982338–JX982365 (Table 2). A COII s = propinv. The node stability of BA trees was evaluated
sequence of the tenebrionid beetle Nesotes helleri (Reitter from their posterior probabilities.
1922) was downloaded from GenBank (A.N.: AJ299304.1)
to be used as out-group in the molecular analyses. Geometric morphometrics
Bayesian (BA) and maximum likelihood (ML) analyses
were performed as implemented in MrBayes 3.1.2 (Huel- The study involved the use of the geometric morphometrics
senbeck and Ronquist 2001) and PhyMl v.3 (Guindon et al. technique, which is nowadays a standard protocol in mor-
2010). For both analyses, the best evolutionary model for phological research. The geometric morphometrics tech-
each dataset was selected using mrModeltest (Nylander niques (Bookstein 1991; Rohlf and Marcus 1993; Adams
2004). According to the Akaike Information Criterion et al. 2004; Zelditch et al. 2004; Viscosi and Cardini 2011)
(AIC), the best-fit model for ML analysis proved to be a were used to quantify and analyze the inter- and intra-
general time-reversible plus invariant sites model specific differentiation in the shape of two external ana-
(GTR ? I); as a measure of branch support, bootstrap tomical structures in the collected Phaleria spp. specimens,
123