Page 13 - Sea-level change_2004
P. 13
ARTICLE IN PRESS
K. Lambeck, A. Purcell / Quaternary Science Reviews 24 (2005) 1969–1988 1981
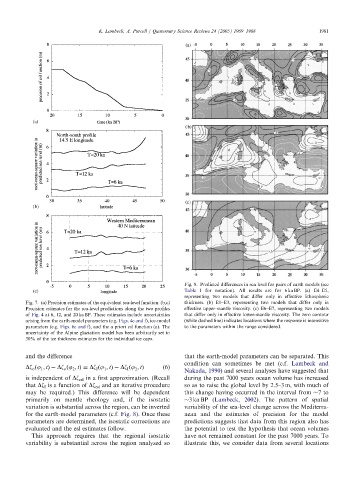
Fig. 8. Predicted differences in sea level for pairs of earth models (see
Table 1 for notation). All results are for 6 ka BP. (a) E4–E5,
representing two models that differ only in effective lithospheric
Fig. 7. (a) Precision estimates of the equivalent sea-level function. (b,c) thickness. (b) E1–E3, representing two models that differ only in
Precision estimates for the sea-level predictions along the two profiles effective upper-mantle viscosity. (c) E6–E7, representing two models
of Fig. 4 at 6, 12, and20 ka BP. These estimates include uncertainties that differ only in effective lower-mantle viscosity. The zero contour
arising from the earth-model parameters (e.g. Figs. 4e andf), ice-model (white dashed line) indicates locations where the response is insensitive
parameters (e.g. Figs. 6e andf), andthe a priori esl function (a). The to the parameters within the range considered.
uncertainty of the Alpine glaciation model has been arbitrarily set to
30% of the ice thickness estimates for the individual ice caps.
andthe difference that the earth-model parameters can be separated. This
condition can sometimes be met (c.f. Lambeck and
Dz o ðj ; tÞ Dz o ðj ; tÞ¼ Dz I ðj ; tÞ Dz I ðj ; tÞ (6)
1 2 1 2 Nakada, 1990) andseveral analyses have suggestedthat
is independent of Dz esl in a first approximation. (Recall during the past 7000 years ocean volume has increased
that Dz I is a function of Dz esl andan iterative procedure so as to raise the global level by 2.5–3 m, with much of
may be required.) This difference will be dependent this change having occurredin the interval from 7to
primarily on mantle rheology and, if the isostatic 3ka BP (Lambeck, 2002). The pattern of spatial
variation is substantial across the region, can be inverted variability of the sea-level change across the Mediterra-
for the earth-model parameters (c.f. Fig. 8). Once these nean andthe estimates of precision for the model
parameters are determined, the isostatic corrections are predictions suggests that data from this region also has
evaluatedandthe esl estimates follow. the potential to test the hypothesis that ocean volumes
This approach requires that the regional isostatic have not remainedconstant for the past 7000 years. To
variability is substantial across the region analyzedso illustrate this, we consider data from several locations