Page 7 - Habitat_Selection_2014
P. 7
Habitat Selection Response of Anchovy and Sardine
The quotient curves relative to bottom depth (Fig. 5) indicate
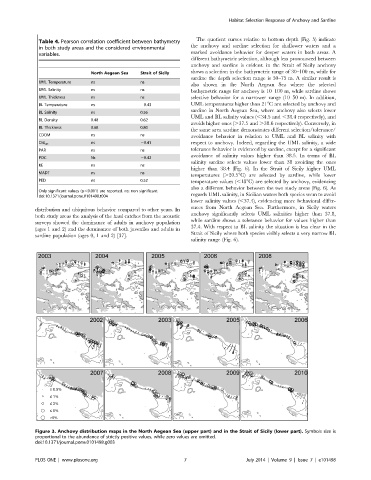
Table 4. Pearson correlation coefficient between bathymetry
in both study areas and the considered environmental the anchovy and sardine selection for shallower waters and a
variables. marked avoidance behavior for deeper waters in both areas. A
different bathymetric selection, although less pronounced between
anchovy and sardine is evident: in the Strait of Sicily anchovy
North Aegean Sea Strait of Sicily shows a selection in the bathymetric range of 30–100 m, while for
sardine the depth selection range is 30–75 m. A similar result is
UML Temperature ns ns
also shown in the North Aegean Sea where the selected
UML Salinity ns ns bathymetric range for anchovy is 10–100 m, while sardine shows
UML Thickness ns ns selective behavior for a narrower range (10–50 m). In addition,
BL Temperature ns 20.43 UML temperatures higher than 21uC are selected by anchovy and
BL Salinity ns 0.56 sardine in North Aegean Sea, where anchovy also selects lower
UML and BL salinity values (,34.5 and ,38.4 respectively), and
BL Density 0.48 0.62
avoids higher ones (.37.5 and .38.6 respectively). Conversely, in
BL Thickness 0.68 0.80
the same area sardine demonstrates different selection/tolerance/
CDOM ns ns avoidance behavior in relation to UML and BL salinity with
ns 20.41
Chl sat respect to anchovy. Indeed, regarding the UML salinity, a wide
PAR ns ns tolerance behavior is evidenced by sardine, except for a significant
avoidance of salinity values higher than 38.5. In terms of BL
POC Ns 20.42
salinity sardine selects values lower than 38 avoiding the ones
KE ns ns
higher than 38.4 (Fig. 6). In the Strait of Sicily higher UML
MADT ns ns
temperatures (.20.5uC) are selected by sardine, while lower
PED ns 0.52 temperature values (,18uC) are selected by anchovy, evidencing
also a different behavior between the two study areas (Fig. 6). As
Only significant values (p,0.001) are reported. ns: non significant.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101498.t004 regards UML salinity, in Sicilian waters both species seem to avoid
lower salinity values (,37.4), evidencing more behavioral differ-
ences from North Aegean Sea. Furthermore, in Sicily waters
distribution and ubiquitous behavior compared to other years. In
anchovy significantly selects UML salinities higher than 37.8,
both study areas the analysis of the haul catches from the acoustic
surveys showed the dominance of adults in anchovy population while sardine shows a tolerance behavior for values higher than
37.4. With respect to BL salinity the situation is less clear in the
(ages 1 and 2) and the dominance of both juveniles and adults in
Strait of Sicily where both species visibly selects a very narrow BL
sardine population (ages 0, 1 and 2) [37].
salinity range (Fig. 6).
Figure 3. Anchovy distribution maps in the North Aegean Sea (upper part) and in the Strait of Sicily (lower part). Symbols size is
proportional to the abundance of strictly positive values, while zero values are omitted.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101498.g003
PLOS ONE | www.plosone.org 7 July 2014 | Volume 9 | Issue 7 | e101498