Page 7 - 2014_A_preliminary_energy
P. 7
48 L. de Santoli et al. / Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 8 (2014) 42–56
Fig. 9. Speed percentage increase vs. inlet speed.
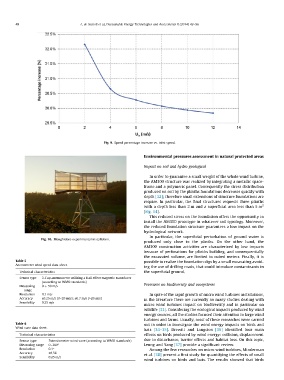
Fig. 10. Monghidoro experimental installation. Environmental pressures assessment in natural protected areas
Table 5 Impact on soil and hydro geological
Anemometer wind speed data sheet.
In order to guarantee a small weight of the whole wind turbine,
Technical characteristics the AM300 structure was realized by integrating a metallic space-
frame and a polymeric panel. Consequently the stress distribution
Sensor type 3-Cup anemometer utilizing a Hall effect magnetic transducer produced on soil by the plinths foundations decreases quickly with
(according to WMO standards) depth [32]; therefore small extensions of structure foundations are
Measuring 0 Ä 50 m/s require. In particular, the final structures requests three plinths
range with a depth less than 2 m and a superficial area less than 5 m2
0.1 m/s (Fig. 14).
Resolution ±0.25 m/s (0–20 m/s); ±0.7 m/s (>20 m/s)
Accuracy 0.25 m/s This reduced stress on the foundation offers the opportunity to
Sensibility install the AM300 prototype in whatever soil typology. Moreover,
the reduced foundation structure guarantees a low impact on the
Table 6 hydrological network.
Wind vane data sheet.
In particular, the superficial perturbation of ground water is
Technical characteristics produced only close to the plinths. On the other hand, the
AM300 construction activities are characterized by low impacts
Sensor type Potentiometer wind vane (according to WMO standards) because of perforations for plinths building, and consequentially
Measuring range 0–360° the excavated volume, are limited to cubed meters. Finally, it is
Resolution 0.1° possible to realize the foundation digs by a small excavating avoid-
Accuracy ±0.5% ing the use of drilling mads, that could introduce contaminants in
Sensibility 0.25 m/s the superficial ground.
Pressures on biodiversity and ecosystems
In spite of the rapid growth of micro wind turbines installations,
in the literature there are currently no many studies dealing with
micro wind turbines impact on biodiversity and in particular on
wildlife [33]. Considering the ecological impacts produced by wind
energy sources, all the studies focused their attention to large wind
turbines and farms. Usually, most of these researches were carried
out in order to investigate the wind energy impacts on birds and
bats [34–35]. Drewitt and Langston [36] identified four main
effects on birds produced by wind energy: collision, displacement
due to disturbance, barrier effects and habitat loss. On this topic,
Leung and Yang [37] provide a significant review.
Among the few researches on micro wind turbines, Minderman
et al. [38] present a first study for quantifying the effects of small
wind turbines on birds and bats. The results showed that birds